News
Site Editor
 Site
/uploads/image/677267645dfcf.png
Compare air domes and traditional domes in terms of design, construction time, costs, flexibility, environmental impact, maintenance, and applications. Learn how air domes offer rapid deployment and adaptability, while traditional domes provide durability and architectural significance.
Site
/uploads/image/677267645dfcf.png
Compare air domes and traditional domes in terms of design, construction time, costs, flexibility, environmental impact, maintenance, and applications. Learn how air domes offer rapid deployment and adaptability, while traditional domes provide durability and architectural significance.
Air Domes vs. Traditional Domes:A Comparative Analysis
Views: 2517
Author: Site Editor
Publish Time: 2024-07-23
Origin: Site
In the realm of modern architecture and construction, domes have long been a symbol of innovation and versatility. However, a newer development in this space is the advent of air domes, which offer a different approach and set of benefits compared to traditional domes. Understanding the distinctions between air domes and traditional domes is essential for appreciating the advancements in construction technology and their implications for various applications.
Structure and Design
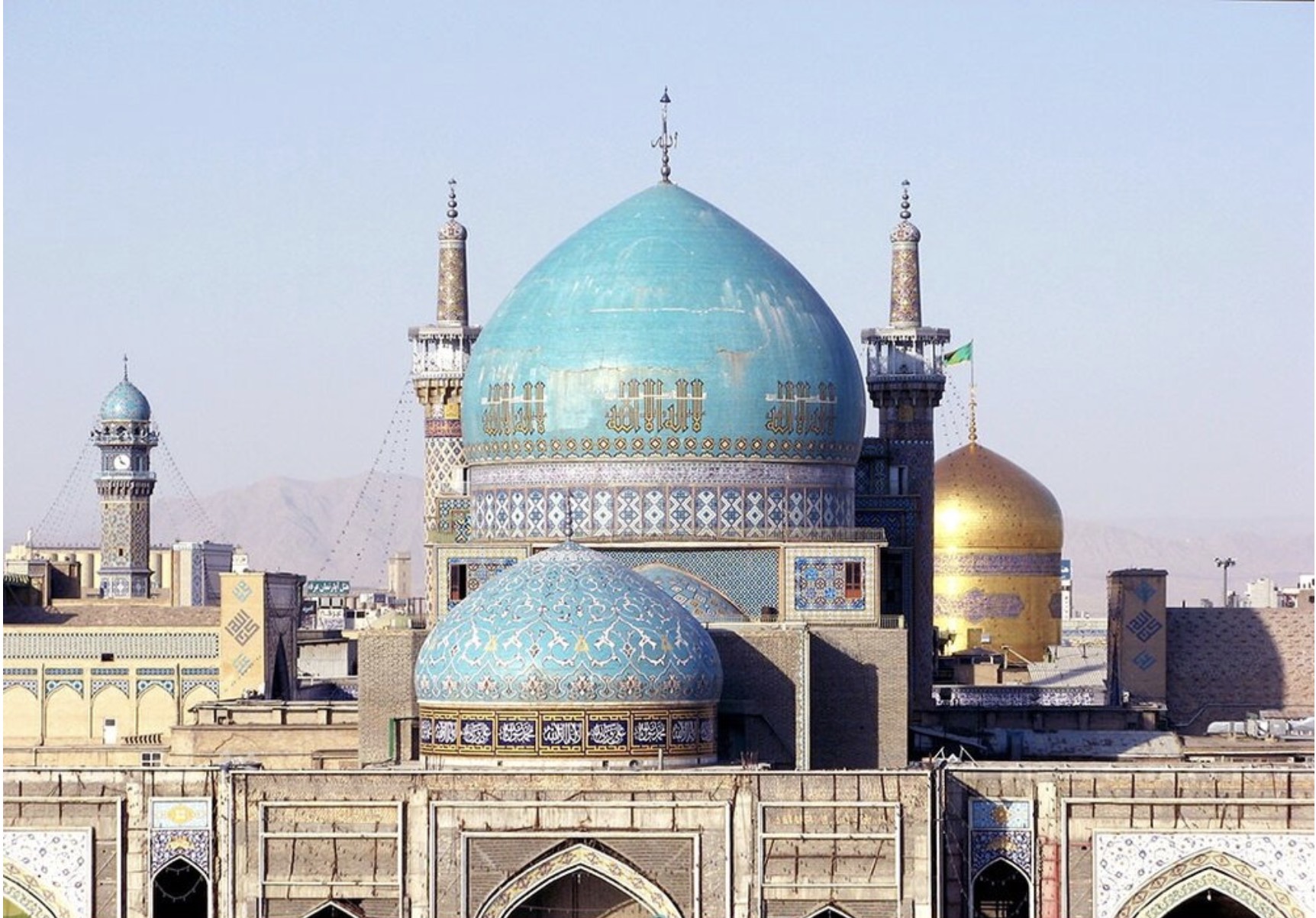
Traditional Domes: Traditional domes are typically constructed using rigid materials such as concrete, steel, or wood. These structures rely on the strength and durability of these materials to maintain their shape and stability. The construction process involves significant labor and time, as each segment of the dome must be precisely engineered and assembled to ensure the structural integrity of the overall design.

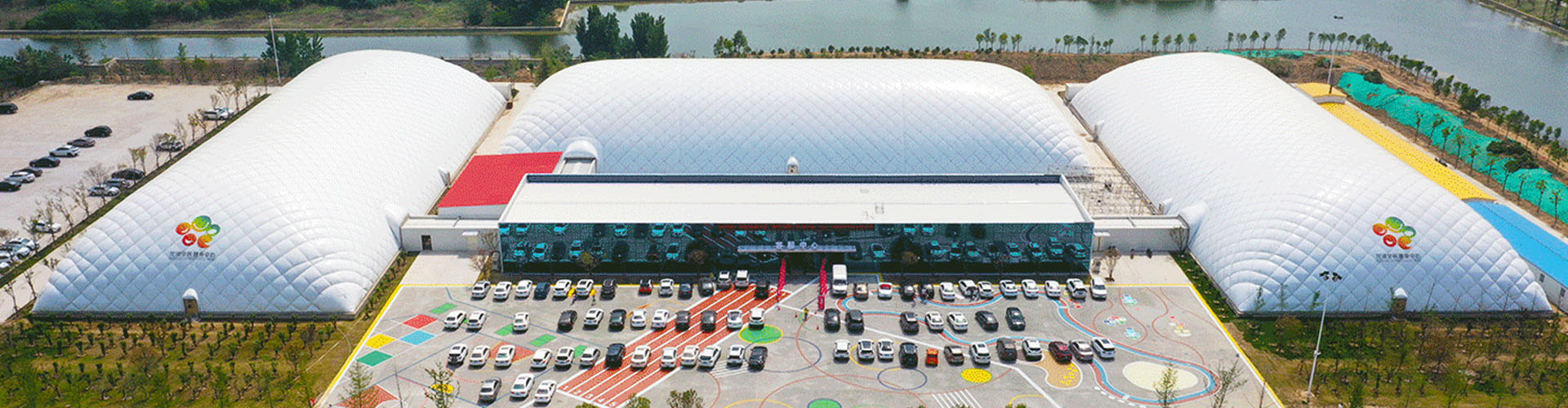
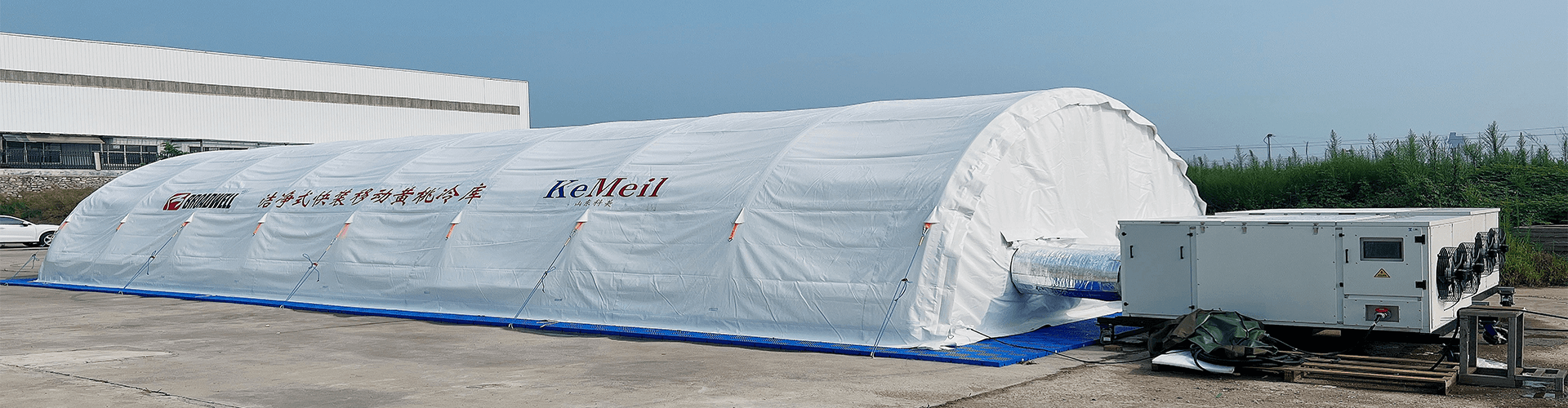
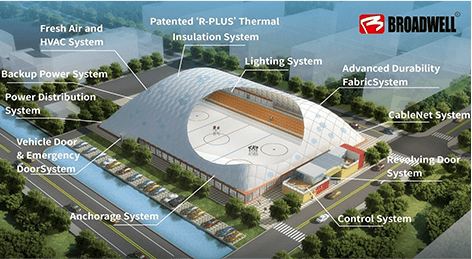
Air Domes: Air domes, on the other hand, are created using flexible, lightweight materials such as PVC-coated polyester fabric. These structures are supported by maintaining a constant internal air pressure, which gives the dome its shape and stability. The air pressure is typically generated by electric blowers, and the structure is anchored to the ground to prevent movement.
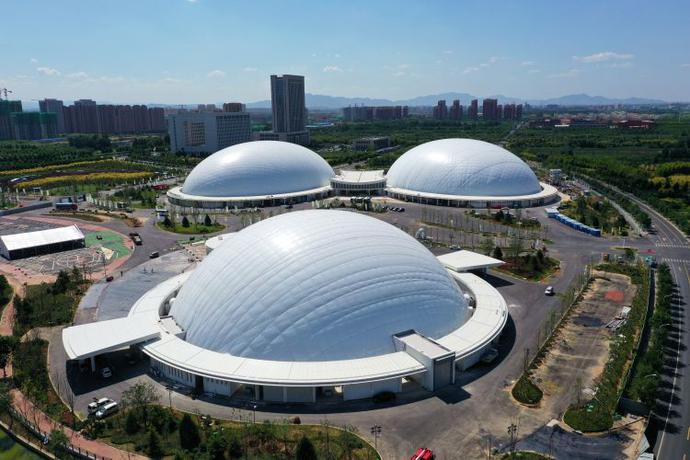

Construction Time and Costs
Traditional Domes: Building a traditional dome is a time-consuming and labor-intensive process. The construction can take months or even years, depending on the size and complexity of the design. The costs associated with traditional domes are also higher due to the extensive use of materials, labor, and the need for heavy machinery.
Air Domes: Air domes offer a significant advantage in terms of construction time and costs. These structures can be erected in a matter of days or weeks, making them ideal for projects that require rapid deployment. The materials used in air domes are generally less expensive, and the construction process requires fewer labor resources and less heavy equipment, leading to lower overall costs.
Flexibility and Adaptability
Traditional Domes: Once constructed, traditional domes are permanent structures. Their rigid nature means they cannot be easily modified or relocated. Any changes to the design or function of the dome typically require extensive renovation or reconstruction, which can be costly and time-consuming.
Air Domes: Air domes are highly flexible and adaptable. They can be easily inflated or deflated, allowing for quick setup and dismantling. This makes them suitable for temporary or seasonal use, as well as for events that require a temporary structure. Additionally, air domes can be relocated to different sites as needed, providing a level of versatility that traditional domes cannot match.
Environmental Impact
Traditional Domes: The construction of traditional domes involves significant use of natural resources and energy. The production and transportation of materials such as concrete and steel contribute to a higher carbon footprint. Furthermore, the construction process itself can have a substantial environmental impact due to the machinery and energy required.
Air Domes: Air domes are designed with sustainability in mind. The materials used are typically recyclable, and the construction process generates less waste and consumes less energy. The use of electric blowers for air pressure is more energy-efficient than the heating and cooling systems required for traditional domes. This results in a lower environmental impact and aligns with modern sustainability goals.
Maintenance and Durability
Traditional Domes: Traditional domes are known for their durability and longevity. With proper maintenance, these structures can last for decades or even centuries. However, maintenance can be complex and costly, involving regular inspections, repairs, and, in some cases, significant restoration efforts.
Air Domes: Air domes have a different maintenance profile. While they may not match the longevity of traditional domes, they are designed for ease of maintenance. Regular inspections of the fabric and air pressure systems are necessary, but repairs are generally straightforward and less costly. The materials used are also resistant to weathering and UV damage, ensuring a reasonable lifespan with proper care.
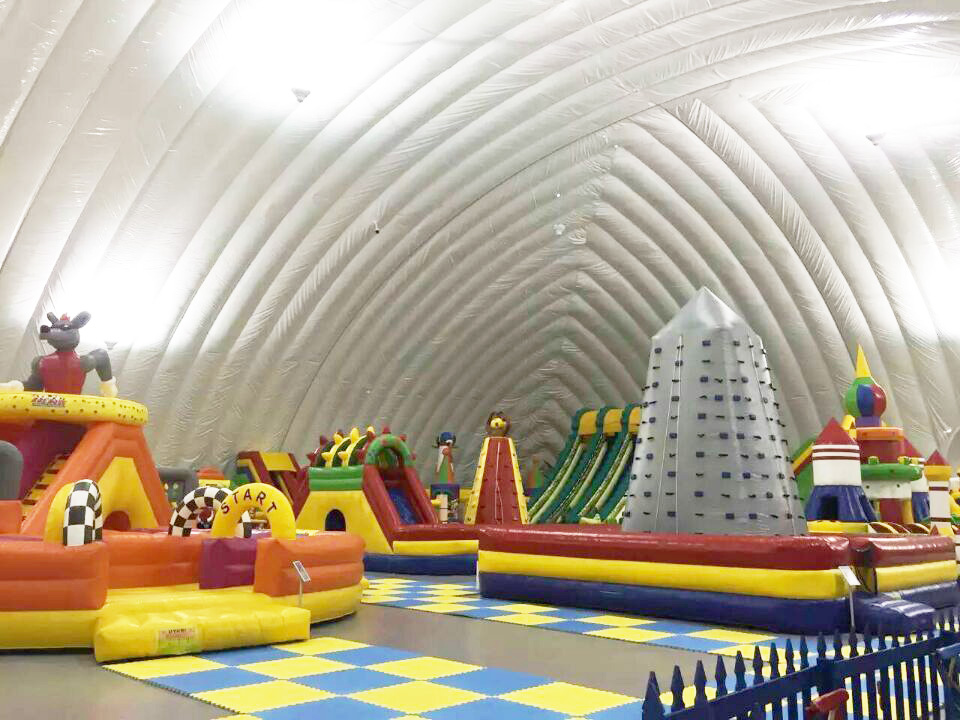

Applications
Traditional Domes: Traditional domes are commonly used in permanent structures such as religious buildings, sports arenas, and government buildings. Their architectural significance and aesthetic appeal make them ideal for landmark structures that are intended to stand the test of time.
Air Domes: Air domes are ideal for a wide range of applications, including sports facilities, temporary event spaces, emergency shelters, and agricultural storage. Their rapid deployment, flexibility, and cost-effectiveness make them suitable for both temporary and semi-permanent uses. They are particularly useful in scenarios where space needs to be quickly created or adapted.
Both air domes and traditional domes offer unique benefits and serve different needs in the construction industry. Traditional domes are celebrated for their durability, aesthetic appeal, and historical significance, while air domes provide a modern alternative that emphasizes flexibility, cost-effectiveness, and environmental sustainability. As technology continues to evolve, the use of air domes is likely to expand, offering innovative solutions for various architectural and engineering challenges.