News
Site Editor
 Site
/uploads/image/677267645dfcf.png
Explore the lifespan of air dome structures – from their historical evolution to key structural components, design considerations, and innovative engineering solutions. Uncover the advantages, applications, and real-world case studies that showcase the durability of air domes. Delve into comparisons with traditional structures, future trends, and potential challenges. This comprehensive article is your guide to understanding the life expectancy of air dome structures for informed decision-making in construction projects
Site
/uploads/image/677267645dfcf.png
Explore the lifespan of air dome structures – from their historical evolution to key structural components, design considerations, and innovative engineering solutions. Uncover the advantages, applications, and real-world case studies that showcase the durability of air domes. Delve into comparisons with traditional structures, future trends, and potential challenges. This comprehensive article is your guide to understanding the life expectancy of air dome structures for informed decision-making in construction projects
What is the life expectancy of an air dome?
Views: 2861
Author: Site Editor
Publish Time: 2023-12-17
Origin: Site
In the early years, pioneers in the field experimented with air-supported enclosures, seeking a balance between structural integrity and cost-effectiveness. Notable milestones include the construction of the first large-scale air dome in the 1960s, demonstrating the viability of this innovative architectural concept. These early projects laid the groundwork for further advancements, as engineers and architects continued refining the design and engineering principles.
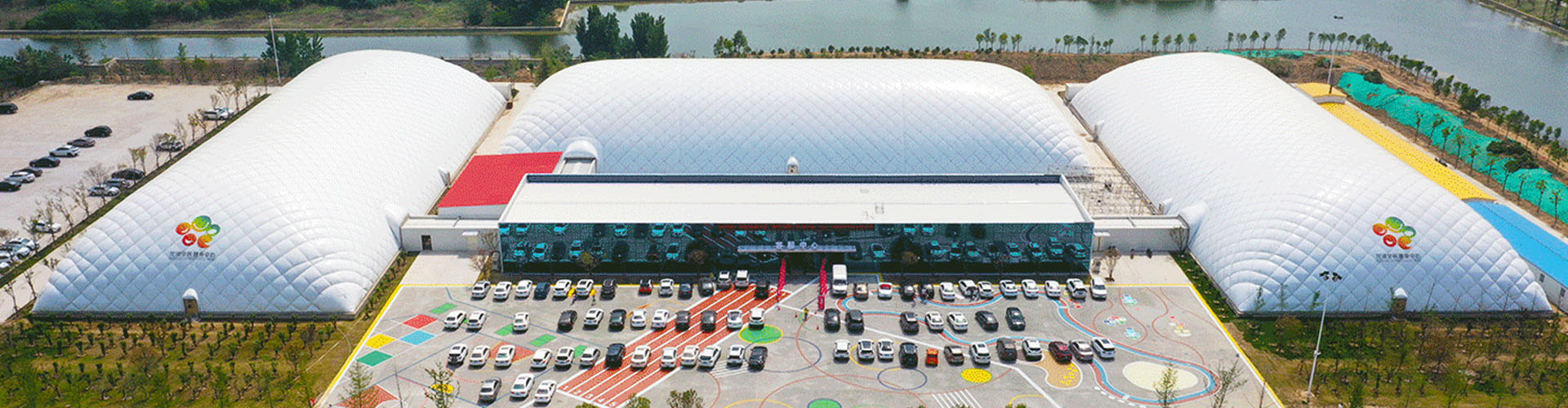
The 1970s witnessed a surge in the popularity of air dome structures, particularly in the realm of sports facilities. The inflatable nature of these structures provided a unique solution for creating expansive, clear-span spaces without the need for extensive supporting columns. This era marked a turning point, solidifying air domes as a practical alternative for diverse applications.
As the technology matured, the 1980s and 1990s saw the construction of larger and more complex air domes, spanning various industries. The newfound adaptability of these structures, coupled with improvements in materials and construction techniques, paved the way for their integration into industrial, commercial, and recreational projects.
Notable projects during this period showcased the resilience and adaptability of air dome structures in adverse weather conditions. The ability to withstand extreme elements became a defining feature, further establishing the credibility of air domes as durable, long-lasting constructions.

Structural Components of Air Dome Structures
Air dome structures, characterized by their innovative design, rely on key structural components to ensure both stability and flexibility. At the heart of these structures is the framework, a carefully engineered system of supports that provides the necessary rigidity. Typically constructed from lightweight materials like steel or aluminum, this framework offers a balance between strength and weight, essential for the overall integrity of the structure.
Complementing the framework is the membrane, the outer covering that encapsulates the air within the dome. High-strength materials such as polyester or fiberglass coated with PVC contribute to the durability of the membrane. The tension within the membrane, maintained by the air pressure, creates a stable structure capable of withstanding various environmental conditions.
Ventilation and climate control systems play a crucial role in regulating the internal environment of air domes. Efficient air circulation not only ensures a comfortable atmosphere but also contributes to the structural longevity by preventing the accumulation of excessive stress on specific areas. Engineers meticulously design these systems to strike a balance between maintaining a stable internal environment and minimizing energy consumption.
Design Considerations
The life expectancy of air dome structures hinges significantly on the thoughtful decisions made during the design phase. One paramount consideration is the intended purpose of the structure. Whether it's a sports facility, an industrial space, or an event venue, the design must align with the specific requirements of the intended use.
Architectural flexibility is a crucial factor. The design should allow for customization without compromising structural integrity. This adaptability ensures that the air dome can evolve with changing needs over time, contributing to its long-term viability.
Aesthetic considerations, while secondary to functionality, should not be overlooked. The design of an air dome structure should harmonize with its surroundings and serve its purpose without sacrificing visual appeal. Striking this balance enhances the structure's overall acceptance and contributes to its sustained relevance.
Additionally, local environmental factors must be meticulously assessed. Factors such as wind load, snow load, and seismic activity play a pivotal role in determining the appropriate design specifications. The design must account for these variables to ensure the longevity and safety of the air dome in its specific location.
Engineering Challenges and Solutions
The durability of air dome structures is intrinsically tied to the ability to overcome inherent engineering challenges. One significant challenge is posed by environmental forces such as wind and snow loads. To address this, engineers employ advanced computational models to simulate and predict how the structure will respond under different conditions. This data informs the design process, allowing for the integration of features that enhance the structure's resilience against varying loads.

Foundation requirements represent another critical consideration. The stability of an air dome relies on a secure foundation, and soil conditions can vary significantly. Engineering solutions often involve thorough soil analysis to determine the appropriate foundation type, whether it be shallow foundations for stable soils or deep foundations for areas with less favorable soil conditions.
Innovative engineering solutions extend to materials used in construction. The selection of high-strength materials for the framework and membrane is paramount. Engineers continually explore materials